OUR LOCATIONS
Call to book 201.523.9590
OUR LOCATIONS
Call to book 201.523.9590
 OUR LOCATIONS
Call to book 201.523.9590
OUR LOCATIONS
Call to book 201.523.9590
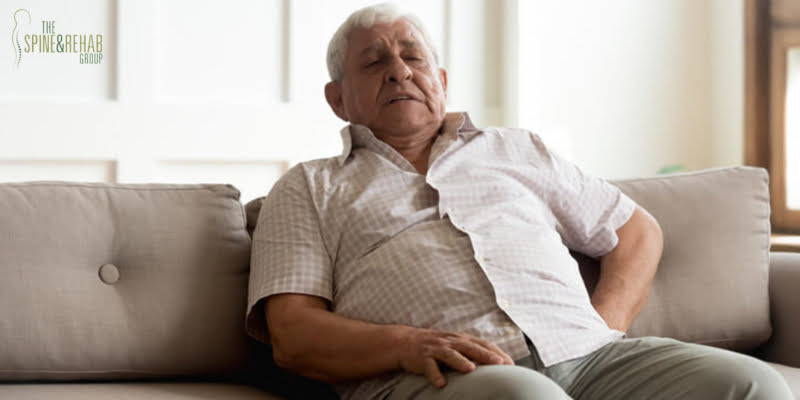


The lungs occupy a significant portion of the chest cavity, with its total size variable on your breathing. This expansion and contraction usually go unnoticed, as your body has a dedicated space and process to account for the activities of your respiratory system. But because it is so interconnected with the muscles in your back and the nerves in your spine, this process can be incredibly sensitive to changes in your body.
So why do people sometimes experience back pain when breathing? Many causes can trigger acute or chronic pain while you breathe, with most causes usually a sign or symptom of a serious condition that needs to be treated right away.
The thoracic area is the longest region and most complex region of the spine, running from the base of the neck down to the abdomen. Because it is the only region in the body that is directly connected to the rib cage, any conditions or complications in this area can affect breathing.
It’s important to remember that the back pain you experience while breathing may not necessarily be caused by the act of breathing itself. There are several triggers that you and your doctor may need to look at before confirming a proper diagnosis of a problem with your thoracic spine area.
Some of these physiological triggers include:
Heartburn, injury, or a slipped disk can all cause back pain that gets worse when you breathe. These conditions may be the primary cause of your back pain, or they may worsen the symptoms like chest tightness and shortness of breath. While it’s possible to attribute back pain to these factors, a full consultation and testing with a medical professional is still the best course of action for a proper diagnosis and treatment options.
In these cases, treatment of the underlying condition usually eases or removes the back pain entirely. Rarely, more serious complications may require extensive amounts of physical therapy or minor corrective surgery.
Patients that use devices like medical harnesses or braces for rehabilitation or physical therapy often experience difficulty breathing in the first few weeks of wearing them. In these cases, adjustments to the brace or harness can easily get rid of the pain and difficulty breathing.
A physician may also recommend different medical harnesses or braces to ensure that patients don’t experience frequent bouts of shortness of breath or thoracic compression. Since these treatments are relatively uncommon, back pain experienced during breathing while wearing them often goes away once the patient acclimatizes to their setup.
Sometimes, improper sleeping position can put undue pressure and misalign the thoracic spine area, which causes them pain and discomfort when they breathe lying down. Depending on the sleeping position, a person may put a significant strain on their diaphragm, which causes them to experience more difficulties breathing.
Rarely, improper sleeping positions can also trigger conditions like a panic attack or anxiety, which can manifest in acute or low-grade chronic back pain. In these cases, doctors will often advise their patients on improvements they can make to their sleep habits, and recommendations on how to improve their posture while asleep.
Even if back pain can differ from patient to patient, there are specific risk factors that can make you more likely to experience back pain while breathing. Some of these causes include:
Added weight around the abdomen, neck, and back can easily put pressure on your muscle groups and nerve clusters, which can cause pain and discomfort while breathing. In serious cases, obese patients can also develop obesity hyperventilation syndrome (also known as Pickwickian syndrome) a condition where the blood lacks oxygen.
A serious cause of back pain while breathing is late-stage lung cancer. Tumors in the lung that press against nerves in the thoracic area can trigger acute pain every time you breathe, laugh, or talk. You may also experience this pain when you swallow food and water or even cough up blood during the evenings.
Kyphosis can often lead to excess pressure on the spine which can compress nerves and leave limited space for your lungs to expand. Aside from causing additional difficulties in breathing because of the increased pressure, severe forms of kyphosis can deform the spine to where the rib cage actually starts poking into the lungs and other internal organs. This tight space coupled with the expansion of the lungs will often cause severe back pain while breathing.
Sometimes, heart attacks may cause pain that radiates from the chest and moves into the back. This back pain can be moderate or severe depending on the heart attack, appearing with other symptoms like fatigue, nausea, pain in the arm, or excessive sweating. These cases are always urgent and should be checked by a doctor immediately.
Scoliosis develops when your spine curves from side to side and usually manifests during adolescence. While the exact causes of scoliosis are difficult to pinpoint, issues with childhood development, genetics, and malnutrition are significant factors. The misalignment of the spine also causes acute back pain and difficulty breathing, though symptoms may not always be noticeable at first.
A fractured vertebra or a bruised and broken limb can also cause back pain while breathing, especially if the injury is near the abdomen. Because of the interconnected system of muscles, tendons, bones, and organs in the thoracic area, any severe or considerable trauma is enough to affect your breathing, even after you recover from the injury itself. In some cases, surgery may be required to alleviate the pain or improve the patient’s quality of life.
A common cause of lower back pain while breathing is a slipped disc, especially if that disk is pressing on a sciatic nerve or your spinal cord. The body’s natural rising and falling during breathing often aggravates a slipped disk, since the vertebra no longer has an outer layer that can withstand the shock. This condition can cause permanent nerve damage if left untreated and may require intense and lengthy physical therapy and surgery.
Intense physical activities or sudden movements may stress or injure muscles to where they overstretch or tear. Depending on the severity of the injury, strained muscles can press into nerve clusters on your back and spinal column, which can cause acute pain whenever you breathe. Typically, these conditions resolve after extended bed rest – though your doctor may check you periodically after the injury has healed to make sure that the area is recovering properly.
Pneumonia is an infection that can cause your lungs to become inflamed and fill up with fluid, which can make it difficult or painful to breathe. Symptoms can range from mild to severe, with the infection being caused by either virus, bacteria, or fungi. Depending on the exact source of your pneumonia, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics, home care, or antifungal medications.
Patients should never self-medicate or try to treat themselves at home when they experience pain while breathing. They should also avoid physical activity that may further strain the area like massages or vigorous exercise unless specifically approved by a medical professional.
Patients that experience back pain while breathing are most likely at risk of developing a serious medical condition and should be examined immediately. While the underlying cause may be trivial, it can quickly escalate in severity and potentially develop into a life-threatening condition if left untreated.
The Spine And Rehab Group has years of extensive experience in diagnosing, treating, and preventing most causes of acute and chronic back pain, with an emphasis on excellent customer service and effective solutions. Our goal of becoming your partner in improving your spinal health has made us one of the leading healthcare specialists in New York, with fast, reliable, and accurate diagnoses that get to the root cause of your problem. Contact us today to set up your consultation.